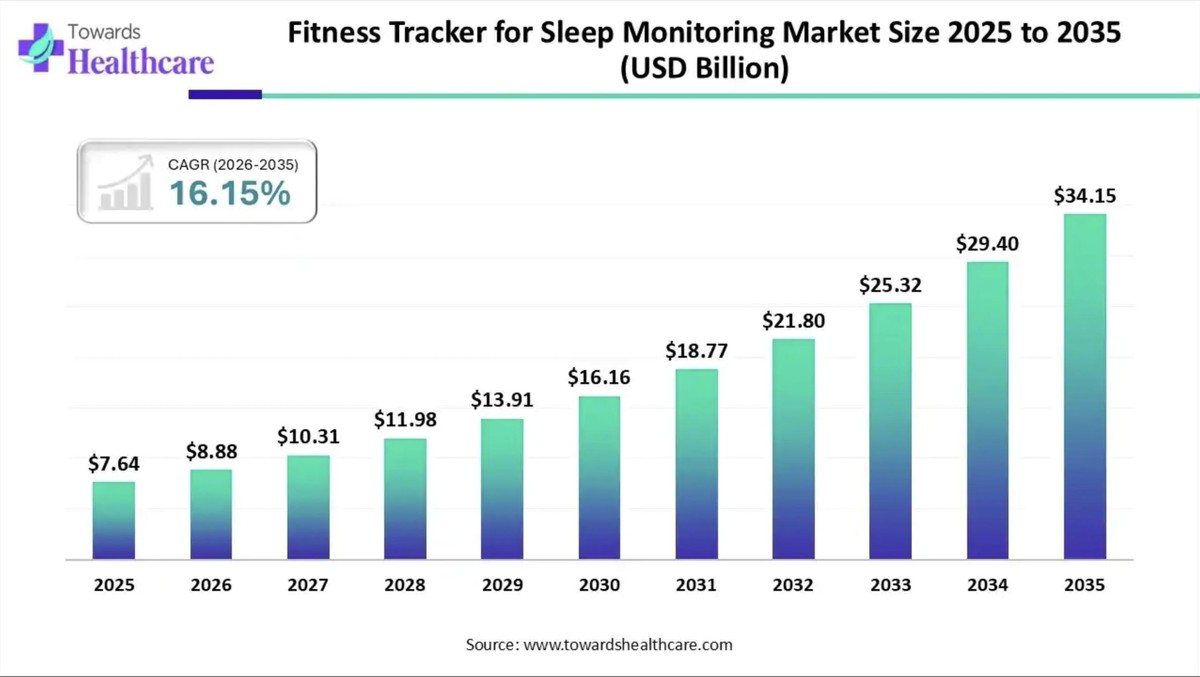
The global fitness tracker for sleep monitoring market is experiencing unprecedented growth, driven by rising health awareness, increasing sleep disorders, and continuous advancements in wearable sensor technology. Valued at USD 8.88 billion in 2026, the market is projected to reach USD 34.15 billion by 2035, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 16.15% over the forecast period.
This explosive growth reflects a fundamental shift in how consumers approach personal health. Sleep tracking has evolved from a novelty feature to an essential health metric, with wearables now capable of monitoring sleep stages, heart rate variability (HRV), blood oxygen (SpO₂), and even respiratory patterns. The convergence of sophisticated sensors, smartphone integration, and AI-driven insights has transformed sleep trackers into comprehensive wellness companions.
Market Drivers and Consumer Trends
The sleep tracker market is being propelled by several interconnected factors. First, awareness of sleep's impact on overall health has skyrocketed. Studies linking poor sleep to cardiovascular issues, cognitive decline, and metabolic disorders have motivated consumers to take a more active role in monitoring their rest patterns. The World Health Organization and various health agencies have emphasized the importance of quality sleep, creating a cultural shift toward data-driven wellness.
Second, the prevalence of sleep disorders is on the rise. Conditions like sleep apnea, insomnia, and restless leg syndrome affect millions globally, driving demand for accessible monitoring solutions. Consumers no longer need to visit sleep clinics for basic assessment—modern fitness trackers provide actionable insights from the comfort of home.
Third, sensor technology has matured significantly. Today's wearables feature photoplethysmography (PPG) sensors for heart rate monitoring, accelerometers for movement detection, and some even include electrodermal activity (EDA) sensors for stress tracking. These components work in concert to deliver increasingly accurate sleep stage classification.
Regional Dynamics: North America Leads, Asia Pacific Surges
North America accounted for the largest market share in 2025, a position driven by high consumer awareness, widespread wearable adoption, and the presence of industry giants like Apple, Garmin, and Fitbit. The region's advanced technological infrastructure, coupled with strong smartphone penetration, created fertile ground for sleep tracking adoption. In the United States specifically, fitness trackers have become mainstream, with users ranging from tech enthusiasts to health-conscious individuals seeking personalized sleep insights.
However, the most dynamic growth is expected in the Asia Pacific region. Countries like China, India, and Southeast Asia are witnessing rapid adoption of wearable technology, supported by rising disposable incomes, expanding e-commerce channels, and growing digital health awareness. Local manufacturers have responded by offering devices with Mandarin interfaces and integrated services tailored to regional preferences. China's wearable market, in particular, has seen aggressive pricing from brands like Xiaomi and Huawei, making sleep tracking accessible to younger consumers and urban professionals.
Segment Analysis: Smartwatches Dominate, Smart Bands Rise
The smartwatch segment dominated the market in 2025 and continues to lead due to its multifunctionality. Modern smartwatches offer continuous sleep tracking alongside heart rate monitoring, activity tracking, GPS, and increasingly, advanced health features like ECG and blood oxygen measurement. This all-in-one proposition appeals to consumers seeking comprehensive health insights without wearing multiple devices.
Apple Watch remains the category leader, especially after its February 2025 software update added sleep stage tracking, respiratory rate monitoring, and personalized sleep schedules through the Health and Sleep apps. The integration with Apple's broader health ecosystem creates a seamless experience that keeps users within the Apple ecosystem.
However, the smart band segment is expected to grow at the fastest CAGR during the forecast period. These devices appeal to cost-conscious consumers and first-time wearable users who want essential sleep tracking without premium pricing. Key advantages include lightweight designs, extended battery life (often 7-14 days on a single charge), and increasingly capable sensors. Xiaomi and Amazfit have dominated this segment with aggressive pricing and feature-rich devices.
Distribution Channels: Online vs. Offline
The online segment dominated distribution in 2025, benefiting from the convenience of e-commerce, competitive pricing, and detailed product comparisons. Platforms like Amazon provide user reviews, spec comparisons, and frequent discounts that drive purchasing decisions. The rise of direct-to-consumer models from brands like Whoop and Garmin has further accelerated online sales.
Yet, the offline segment is projected to grow at the fastest rate going forward. Many consumers prefer to try wearables before purchasing, especially for devices that require proper fit for accurate sensor readings. Specialty retailers and electronics stores offer hands-on demonstrations, personalized fitting, and after-sales support that builds consumer confidence. This trend is particularly strong in emerging markets where brick-and-mortar retail is expanding rapidly.
Key Players and Competitive Landscape
The sleep tracker market features a diverse competitive landscape:
Apple continues to lead the premium segment with Apple Watch integration, offering sleep tracking alongside comprehensive health monitoring through the Health app ecosystem.
Garmin positions itself at the intersection of fitness and health, with devices targeting both casual users and serious athletes. The announced Garmin Index Sleep Monitor represents an interesting diversification—a screenless upper-arm tracker focused specifically on sleep accuracy.
Samsung has strengthened its offerings through the Galaxy Ring and Galaxy Watch lineup, adding features like Sleep Environment Report and Sleep Time Guidance to Samsung Health.
Fitbit (Google) remains a major player, particularly in the fitness band segment, with established sleep tracking algorithms and a strong brand identity around wellness.
Xiaomi and Amazfit dominate the value segment, offering capable sleep tracking at price points accessible to mass markets.
Whoop has carved a niche in performance-focused sleep analytics, emphasizing recovery metrics and strain tracking for athletes.
Huawei continues expanding its wearable lineup with health monitoring features, despite market challenges in certain regions.
Emerging Challenges
Despite the optimistic outlook, manufacturers face significant challenges. Sleep tracking accuracy remains inconsistent across devices and users, as sensor performance can vary based on skin tone, body composition, and wearing position. The industry continues to grapple with balancing consumer expectations for medical-grade accuracy against the limitations of consumer-grade sensors.
Privacy concerns also loom large. Sleep data reveals intimate details about users' lives—their schedules, health conditions, and daily routines. Companies must demonstrate robust data protection practices to maintain consumer trust, especially as health data becomes increasingly valuable to insurers and employers.
Technology Deep Dive: How Sleep Tracking Works
Modern fitness trackers employ multiple sensor technologies to capture sleep data. The primary sensor is the optical heart rate monitor using photoplethysmography (PPG), which measures blood volume changes through the skin. By analyzing heart rate variability—the time interval between consecutive heartbeats—algorithms can distinguish between light sleep, deep sleep, and REM stages.
Accelerometers complement PPG sensors by detecting movement throughout the night. When combined with heart rate data, this movement information helps refine sleep stage classification. Some advanced devices also incorporate ambient light sensors to detect sleep environment conditions.
More recent innovations include temperature sensors that track skin temperature fluctuations, which correlate with circadian rhythms and can indicate ovulation or illness. Some wearables now include galvanic skin response (GSR) sensors that measure electrical conductivity changes linked to stress and emotional arousal.
The software side has evolved equally dramatically. Machine learning models trained on millions of sleep records can now achieve accuracy rates exceeding 80% compared to polysomnography (PSG) lab equipment, though significant variation exists between devices and individual users.
What This Means for Consumers
For everyday users, the implications are significant. Sleep trackers provide objective data about habits that were previously difficult to quantify. By revealing patterns—the impact of late-night screen time, alcohol consumption, or irregular schedules—these devices empower users to make informed lifestyle adjustments.
However, experts caution against becoming overly fixated on numbers. Sleep quality is subjective, and a device that reports "poor" sleep may not align with how refreshed someone actually feels. The best approach uses tracker data as one input among many, not as the definitive measure of rest quality.
For athletes, sleep tracking has become essential to training optimization. Companies like Whoop and Garmin emphasize recovery metrics, using HRV to determine whether the body is primed for intense training or needs rest. This quantified approach to recovery has revolutionized how coaches and athletes periodize training cycles.
The Future of Sleep Tracking
Looking toward 2035, several trends will shape the market. Integration with smart home devices is accelerating—beds that adjust firmness based on sleep data, thermostats that optimize bedroom temperature, and lighting systems that align with circadian rhythms will create holistic sleep environments.
Medical-grade sleep monitoring is another frontier. While consumer devices cannot diagnose sleep disorders, they serve as valuable screening tools. Companies are exploring partnerships with healthcare providers to create pathways for users with suspected sleep apnea or other conditions to receive professional evaluation.
Continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) represent another convergence point. Though primarily designed for diabetes management, these devices generate data relevant to sleep—blood sugar fluctuations can significantly impact rest quality. Some users already combine CGMs with fitness trackers for comprehensive metabolic monitoring.
The sleep tracker market's trajectory reflects broader societal priorities shifting toward preventive health and quantified self-improvement. At $8.88 billion today and projected to exceed $34 billion by 2035, the opportunity is substantial. For consumers, this means increasingly sophisticated devices at various price points. For manufacturers, the challenge is balancing innovation with accessibility while addressing the very real concerns around accuracy and privacy that come with monitoring something as intimate as sleep.